|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
August 2, 1992 |
vs. Iraq |
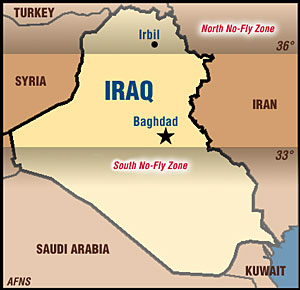
Establishment of "no-fly zone". |
The "no-fly zone" is imposed over south Iraq as a means of halting air attacks on Shiite Muslim rebels. The United States begins air patrols of the zone. |
|
|
December 28, 1992 |
vs. Iraq |
Air combat to enforce Operation Southern Watch "no-fly zone." |
A US plane shoots down an Iraqi Mig-25 when it enters the "no-fly zone." |
|
|
January 13, 1993 |
vs. Iraq |
Retaliatory air and missile strike. |
Gulf coalition forces strike Iraqi radar and missile sites near the cities of Nasiriyah, Samawa, Najaf and Al Amara. Over 100 aircraft take part in these attacks. |
|
|
January 17, 1993 |
vs. Iraq |
Retaliatory missile strike. |
The United States struck the Zafraniyah Nuclear Fabrication Facility, near Baghdad, with up to 42 Tomahawk Cruise missiles. This strike was designed to punish Saddam Hussein for Iraq's non-compliance with United Nations weapons inspections. |
|
|
June 27, 1993 |
vs. Iraq |
Retaliatory air strike. |
The United States fires 24 cruise missiles from two US Navy ships at an intelligence headquarters in Baghdad. Iraq claims eight people are killed in the assault. President Clinton ordered this attack as retaliation for an alleged plot to assassinate former President George Bush on a trip to Kuwait. |
|
|
October 7, 1994 |
vs. Iraq |
Military buildup due to renewed crisis. |
US planes and 54,000 troops head for the Gulf as Iraq's troops appear to be on the verge of launching an offensive on Kuwait. Crisis is averted as Iraq pulls back its army. |
|
|
August 31, 1996 |
vs. PUK (Kurdish Faction) |
Iraqi army support for one side in Kurdish civil war inside "protected area" in Northern Iraq. |
Iraq seizes the city of Irbil inside the Kurdish "safe haven" protected by US-led troops. |
|
Operation Desert Strike |
September 3 and 4, 1996 |
vs. Iraq |
Retaliatory missile strike in response to Iraqi military actions. |
The United States fires 44 Tomahawk cruise missiles at Iraqi military targets. President Clinton extends the "no-fly zone" to cover parts of Baghdad and central Iraq. |
|
|
December 16 through December 20, 1998 |
vs. Iraq |
Retaliatory missile and air strikes to punish Iraq for non-cooperation with UNSCOM's inspections. |
The U.S. and Britain attacked sites related to the production of nuclear, chemical and biological weapons. Targets hit included airfields, military command centers, suspected missile factories and an oil refinery. Bases and headquarters for Saddam's Republican Guard were also hit. As a result of these attacks, the Iraqi government declared an end to all UNSCOM inspections and said it would militarily challenge the "no-fly" zones. |
|
|
December 29, 1998 |
vs. Iraq |
Iraqi missile batteries fired on U.S. aircraft over the northern "no-fly" zone. |
The Allied warcraft returned fire and destroyed the Iraqi air-defense battery. |
|
|
December 30, 1998 |
vs. Iraq |
Iraqi missile batteries fired on U.S. and British aircraft over the southern "no-fly" zone. |
The Allied warcraft returned fire and destroyed the Iraqi air-defense battery. |
|
|
December 30, 1998- March 19, 2003 |
vs. Iraq |
Continued bomb and missile attacks by the U.S. and Britain. |
Since Desert Fox, the Allies have engaged in almost daily attacks as Iraq attempts to enforce its sovereignty over the "no-fly" zones. After Desert Fox, Iraq ejected all UN inspectors and declared the "no-fly" zones to be illegal. Violence increased as tensions mounted during the lead-in to the 2003 Invasion of Iraq. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
*Note: It was reported that when the NATO assaults on Yugoslavia/Serbia began in the Kosovo War, Iraq and Yugoslavia communicated information regarding U.S. and British air tactics. Also, unconfirmed reports indicate that the two nations traded and/or sold to each other military hardware.
1. In effect, the Gulf War never really ended, but merely shifted into a type of cold war, with lots of yelling, threats and rhetoric interspersed with a few brief moments of violence. Since December of 1998, the violence has escalated markedly.
2. Continued tension in the Gulf region. This has the effect of disrupting the worldwide oil markets and has also disrupted stock exchanges around the globe.
3. A continued drain on the military resources of the United States and other Gulf Coalition allies. Increasing criticism of the Gulf monarchies who allow Coalition forces to use their countries as staging areas for action against Iraq.
4. As a result of the economic embargo against their nation, the Iraqi people have suffered greatly. The nation's infrastructure is collapsing and thousands of children have died as the poorer elements of the society are hit by the sanctions.
Iraq-- Several dozen military casualties resulting from air attacks. Civilian deaths due to the sanctions run into the thousands. Exact figures are not available. Operation Desert Fox was first reported by Iraq to have killed "thousands" of people, but newer numbers indicate casualties in the low hundreds.
Gulf Coalition Allies -- No reported casualties from Iraqi fire.
1.
Kohn, George C. Dictionary
of Wars. New
York: Facts On File Publications, 1999.
News Links
U.S. Bombing Watch--A compilation of data on U.S. air strikes on Iraq.
Yahoo! Full Coverage of the Iraq-U.S. Conflict.
New York Times: Issues In Depth: Attack on Iraq--News source on the Iraq conflict.
BBC News: Iraq - Years of tension: 1992-96--Background information from the British Broadcasting Corporation on the ongoing conflict between Iraq and the UN
Confrontations Since the Gulf War-- Very detailed listing of ALL Iraq-U.S./UN confrontations since 1991. Tons of facts available on this site.
Arabic News-- News from the Arab World.
IraqNet News Center-- Good resource for finding news and other links on Iraq and the Middle East.
The History Guy: Issues: Iraq-U.S. Conflict--The History Guy's page containing links to many Iraq sources. Part of this website's Politics section.
Iraq chronology-- Well-detailed site listing significant actions from December of 1998 to June of 1999.
The Iraq Foundation --"is a non-profit, non-governmental organization working for democracy and human rights in Iraq, and for a better international understanding of Iraq's potential as a contributor to political stability and economic progress in the Middle East."*Descriptive statement is from the Iraq Foundation website.
DOD 101: United States Military Operations-- Fascinating website run by the Federation of American Scientists. On this site you will find tons of data on US military operations going back decades.
Iraq History-- A very detailed accounting of Iraqi/Mesopotamian history covering Biblical times to the Present.
UNSCOM-- The United Nations Special Commission, the organization that conducts the weapons inspections in Iraq. This page is part of the UN website.
Iraqi Rulers--Part of the Iraq4ever website. Lists the rulers of Iraq from independence to the present.
Iraq History--Part of the Iraq4ever website. Includes quite a bit of detail on the history of Iraq and the Mesopotamia region.
Iraq Action Coalition--"The Iraq Action Coalition (IAC) is an independent grassroots coalition dedicated to ending the war on the people of Iraq. IAC provides information and analysis on the devastating effects of the continuing war (sanctions)." **Descriptive statement taken from IAC Homepage.**
The Sanctions War Is Killing Iraqi Children--Page detailing the suffering of Iraqi children resulting from the economic sanctions. Part of IAC website.
Iraq Crisis Antiwar Homepage--
Physicians for Global Survival (PGS): The Gulf War of 1991 Sanctions and Iraq--Site maintained by a physicians anti-war organization. Contains many interesting links.
Siahkal News: Wars--Web page devoted to news and politics from Iran. This page deals with the war in neighboring Iraq.
Resolution 1137 - Nov. 12, 1997
Approves travel sanctions against senior Iraqi officials.
Resolution 1134 & Resolution 1115 - Oct. 23 & June 21, 1997
Demand that Iraq cooperate fully with the inspections regime.
Resolution 986 - April 14, 1995
Approves sale of Iraqi oil for food and humanitarian relief.
Resolution 687 - April 3, 1991
Formally ends the 1991 Persian Gulf War and authorizes the inspection and elimination of Iraq's suspected weapons of mass destruction.
Resolution 661 - Aug. 6, 1990
Imposes a trade and financial embargo on Iraq and occupied Kuwait. Establishes a special sanctions committee to implement the resolution and calls upon U.N. members to protect the assets of Kuwait around the world.
Resolution 660 - Aug. 2, 1990
Condemns the invasion of Kuwait, demands Iraq's unconditional, immediate withdrawal and calls on both countries to begin negotiations.
Copyright © 1998-2016 History Guy Media 11.12.16
"The History Guy" is a Registered Trademark.
History Guy SiteMap